The default SSH port can be changed by server administrators for various reasons. The main reasons for changing the port are as follows:
- Security Measure:
Default SSH ports are constantly scanned by bots on the internet. This causes systems using the standard port to be frequently targeted by password-guessing attacks. To enhance security, server administrators may change the SSH port to reduce the risk of such attacks. - Network Restrictions:
In some organizations or networks, the use of standard ports may be blocked for security reasons. In such cases, a different port must be selected to establish an SSH connection. - Preventing Port Conflicts:
If another service on the server uses the same port, the SSH port may be changed to prevent conflicts.
For the reasons mentioned above or similar ones you can follow the steps below to safely change your SSH port.
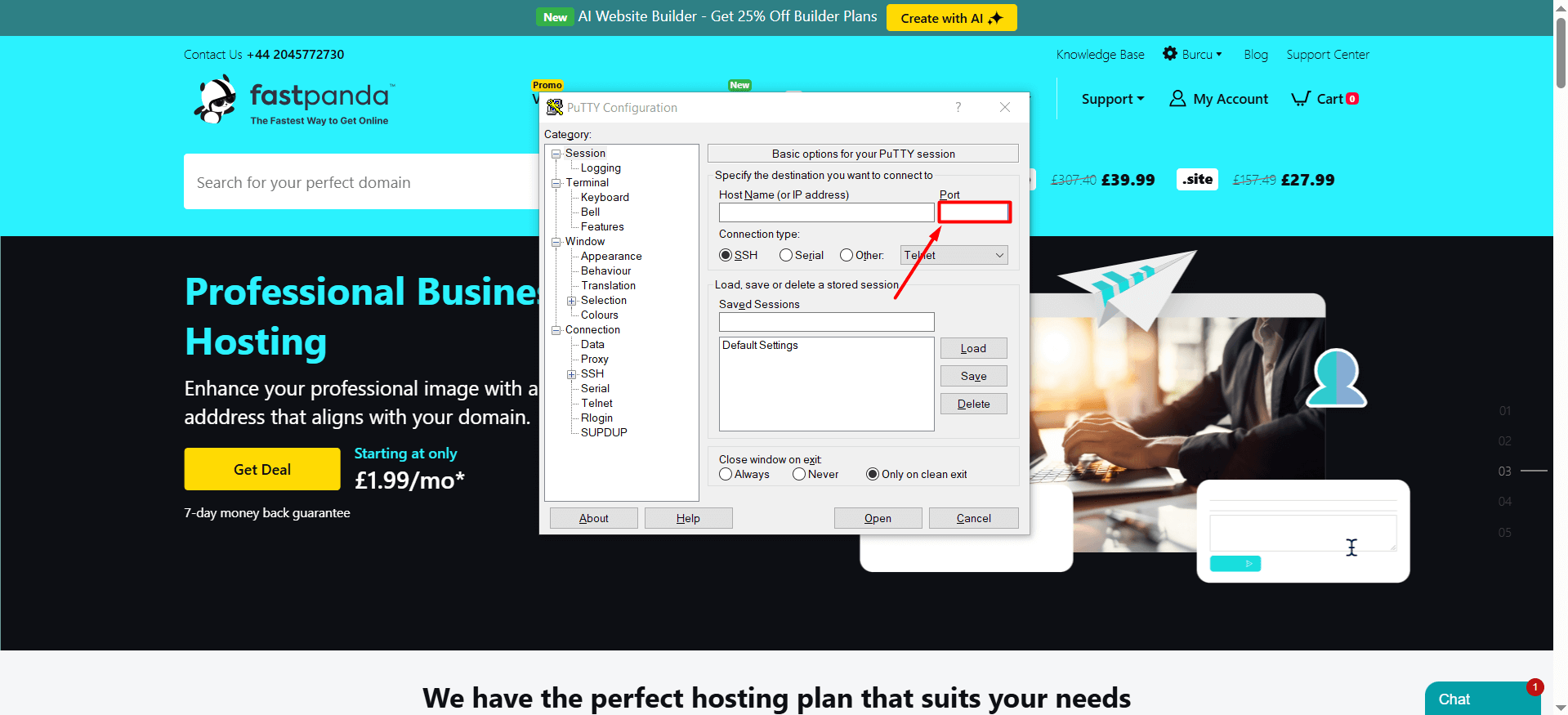
- Log in to the server. If you are not familiar with the steps to access the server, click here to read our guide. The following steps use PuTTY as an example.
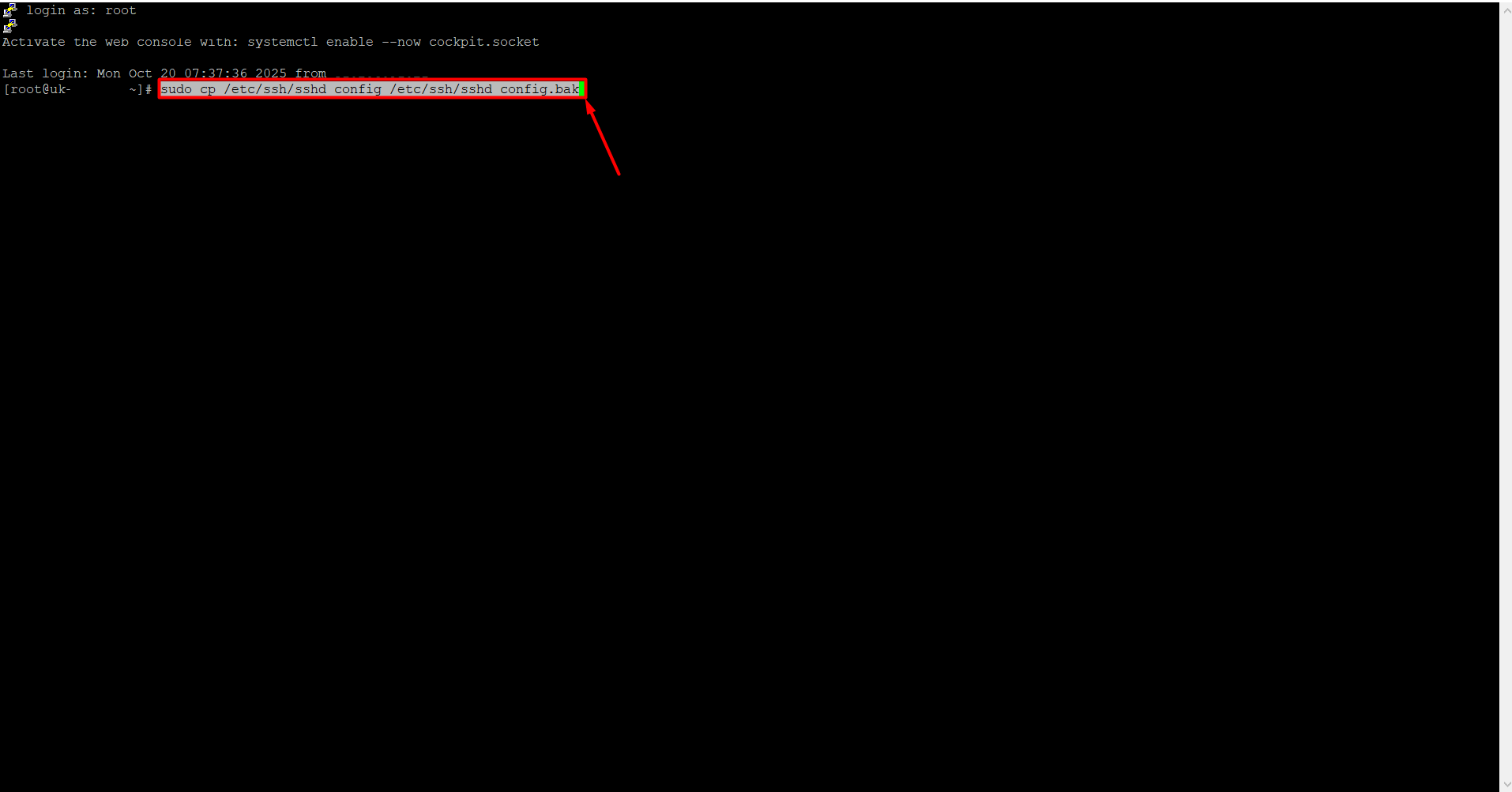
- Back up the sshd_config file. Since you will be making changes to the port and security settings, any mistake could prevent you from accessing the server via SSH. Therefore, it is recommended to create a backup beforehand. To back it up, copy the command below, right-click to paste it into the server after connecting, and press Enter.
sudo cp /etc/ssh/sshd_config /etc/ssh/sshd_config.bak
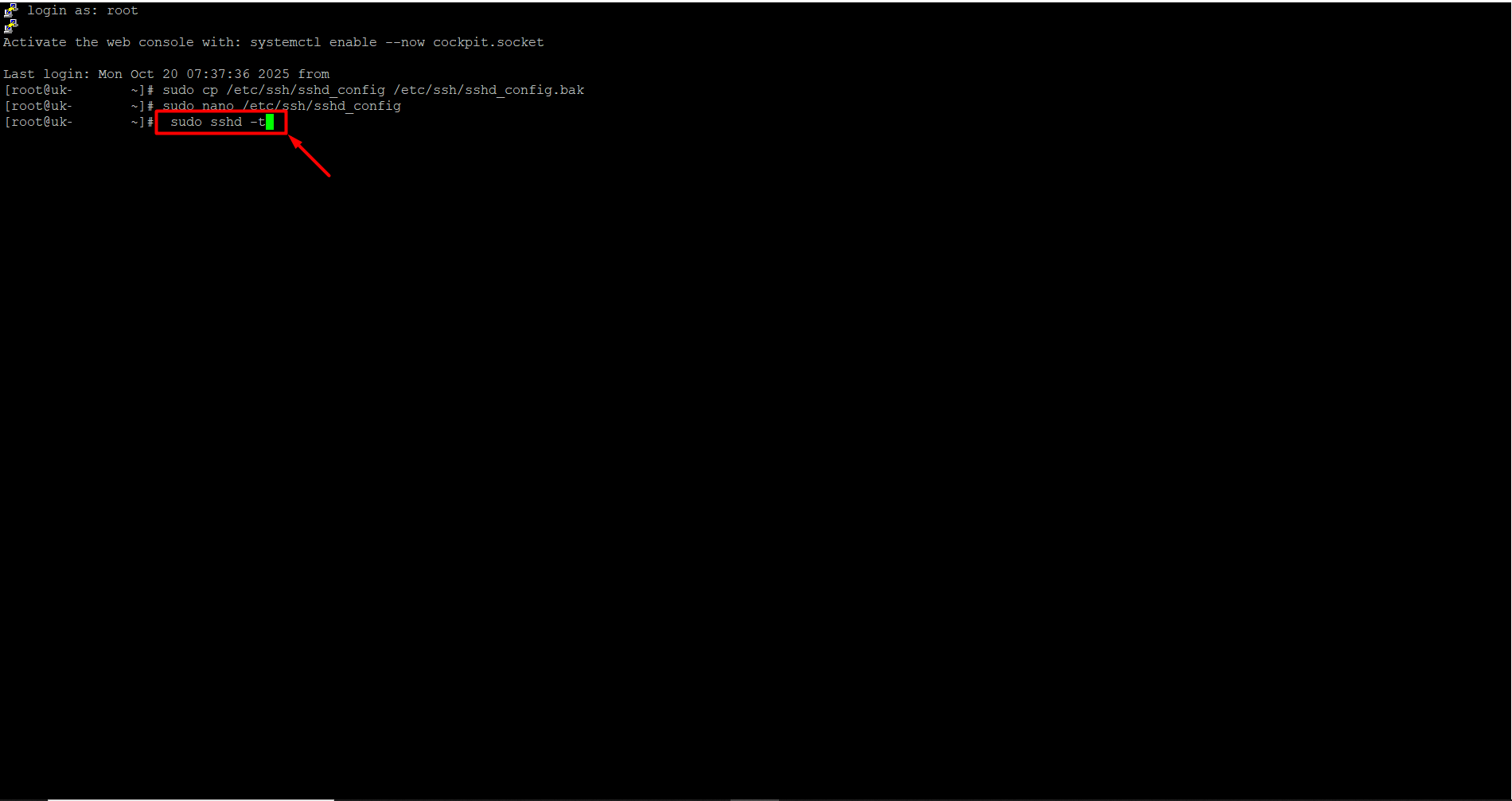
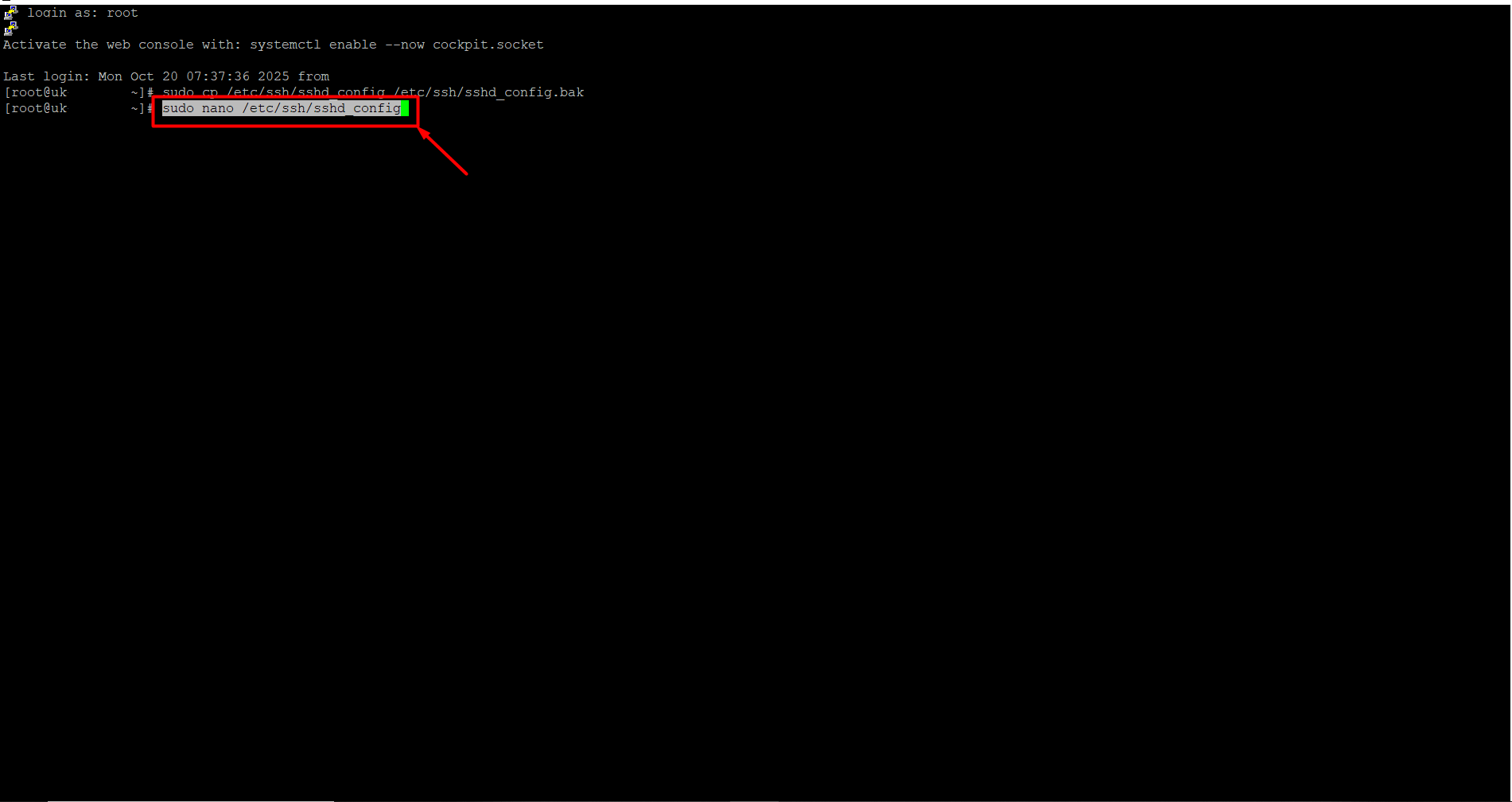
- To open the SSH configuration file, copy the command below, right-click to paste it into the server, and press Enter.
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
-
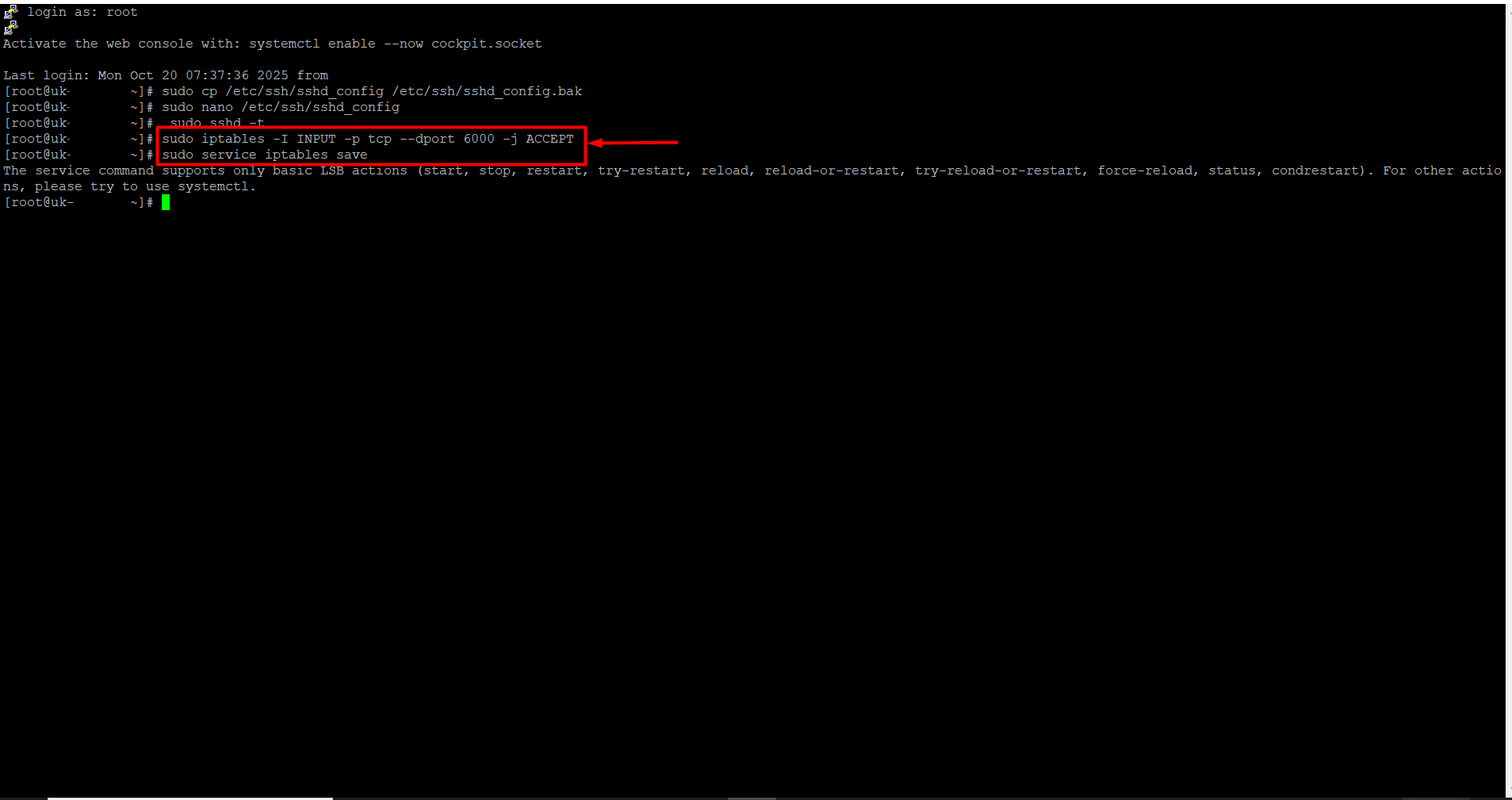
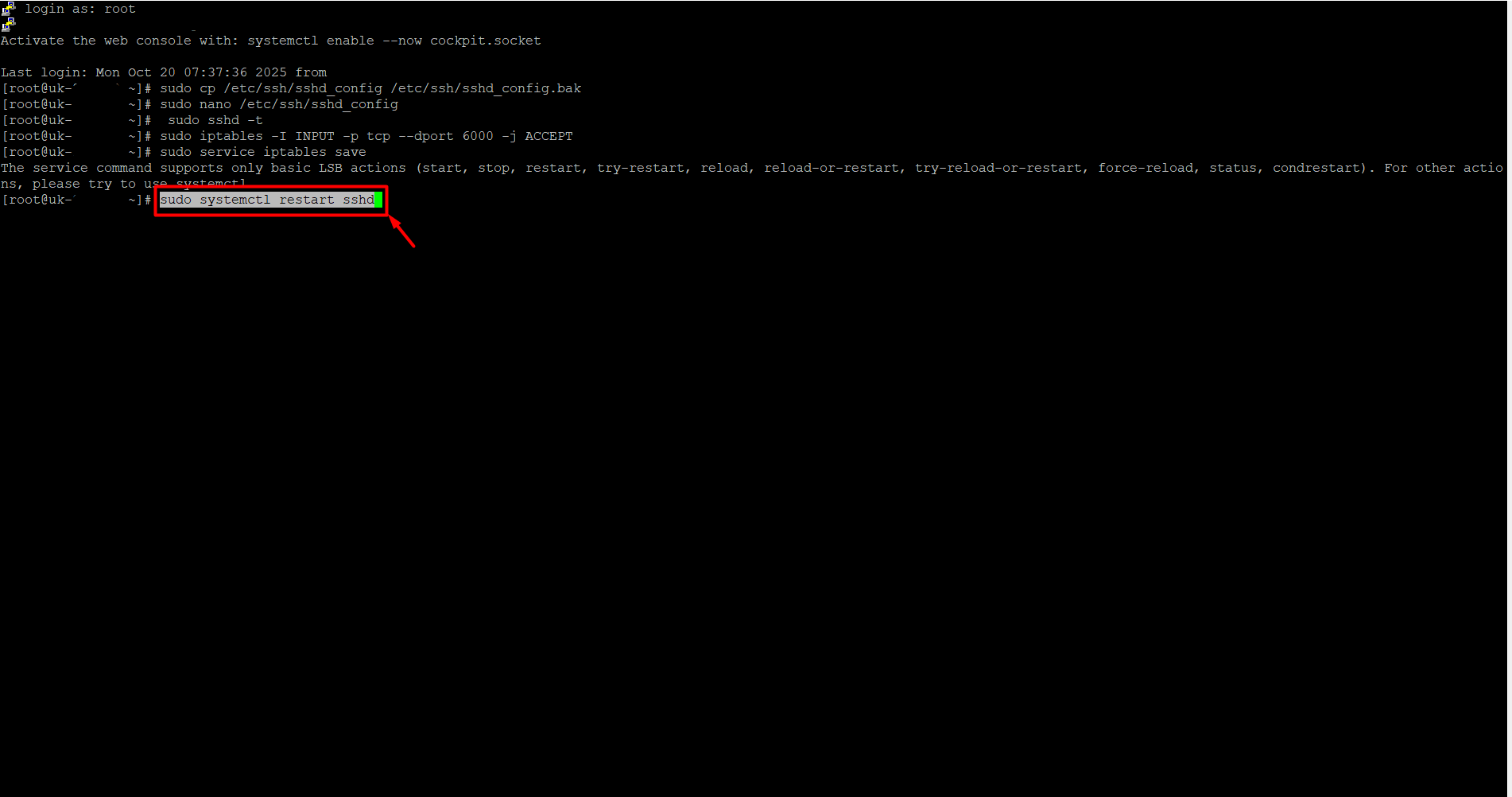
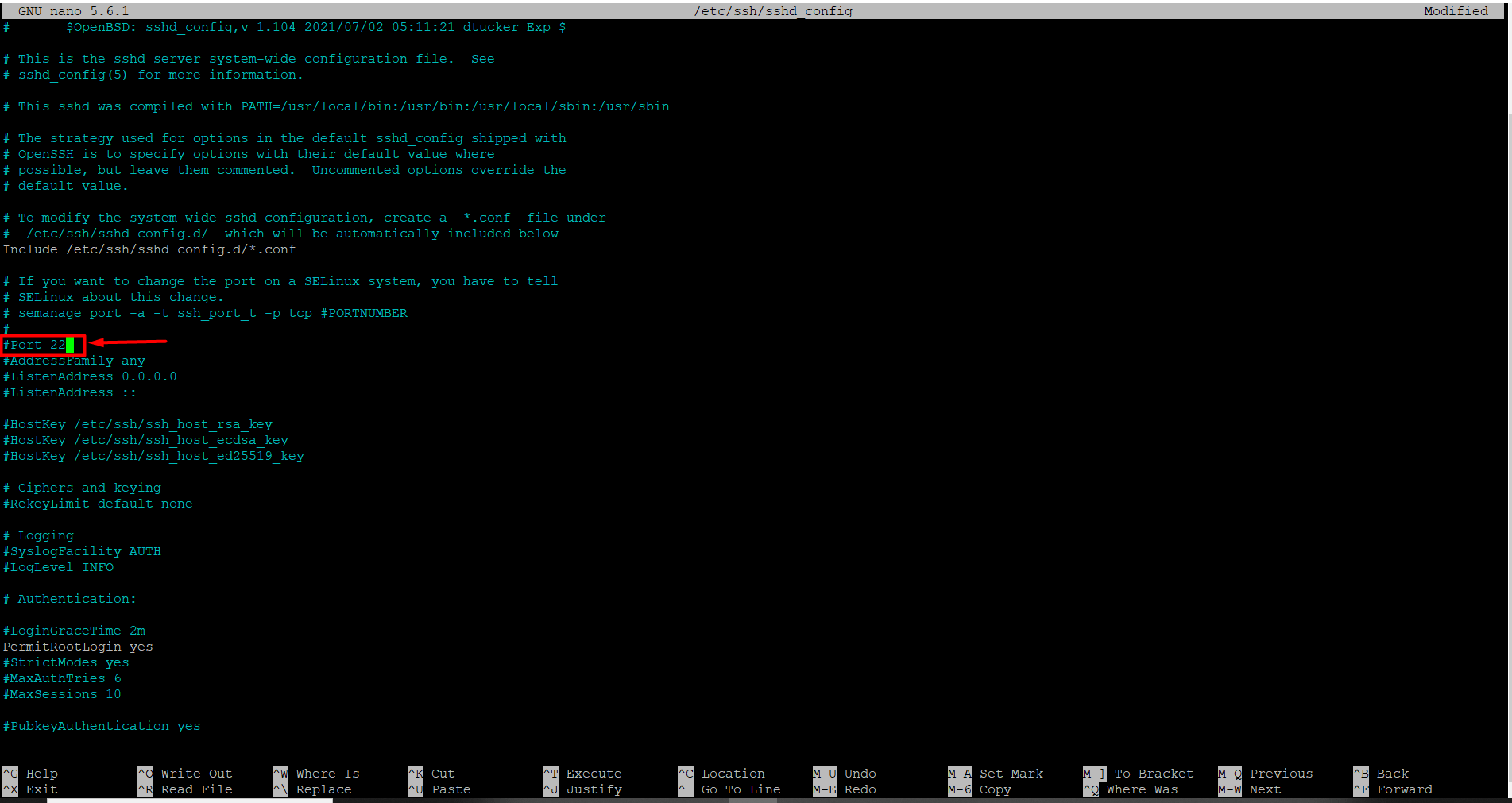
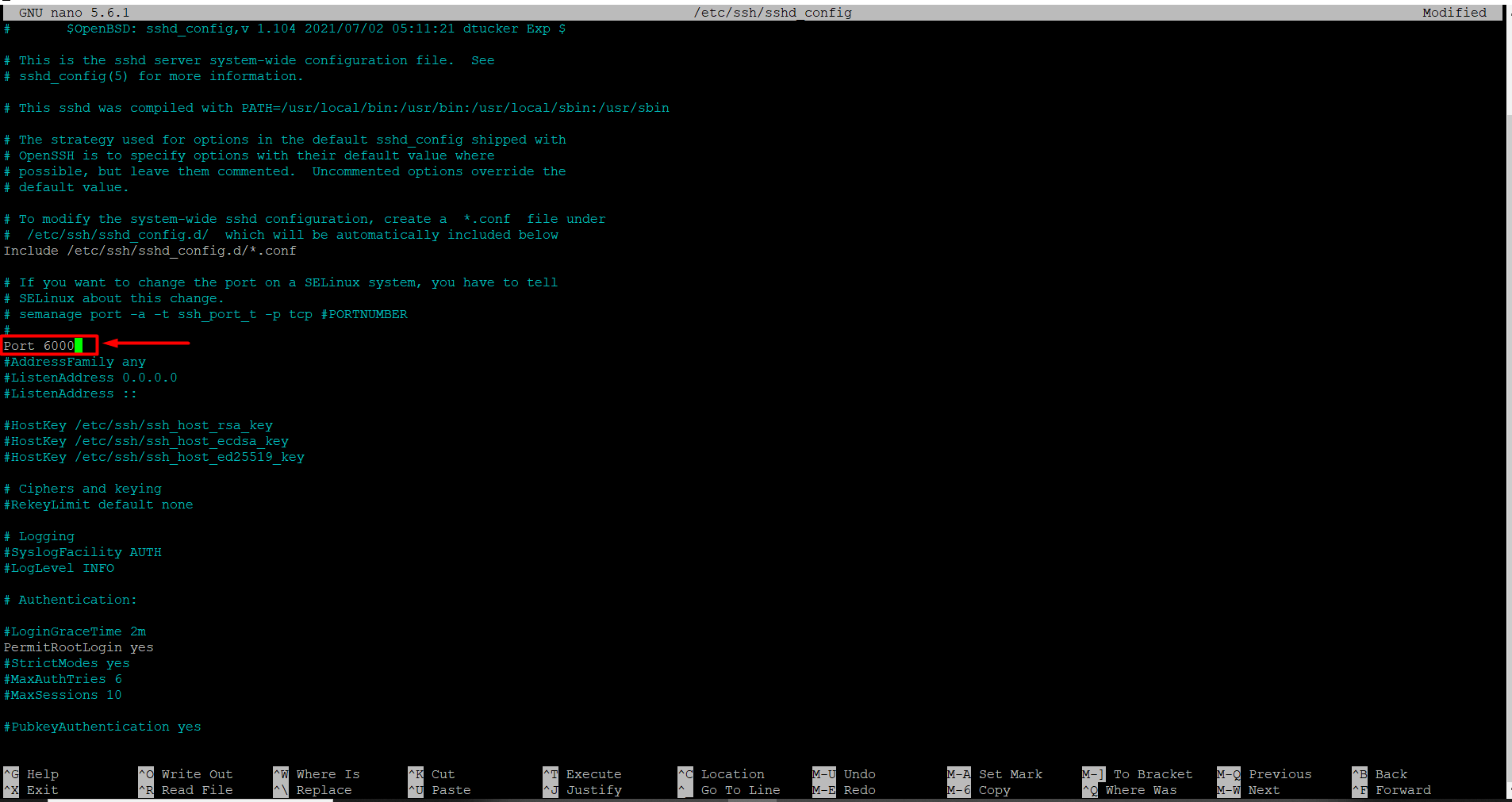
Locate the line in the file that says “Port 22” or “Port 22667”. (You may see a different port number instead of 22 or 22667.) Replace 22 or 22667 with the port number you want, for example, 6000.If there is a “#” at the beginning of the Port line, remove it, because # is treated as a comment and the new port may not take effect. To save, press Ctrl + O and then Enter. Immediately after, press Ctrl + X to exit.
-
Valid range: 0 – 65535
-
0 – 1023: Reserved for the operating system and core services. Manual use is not recommended. Examples: 22 and 22667 (SSH), 80 (HTTP), 443 (HTTPS)
-
1024 – 49151: Registered ports used by software; usually okay to use. Examples: 3306 (MySQL), 3389 (RDP)
-
49152 – 65535: Usually free ports. This range is the safest choice for your own services.
-













 .CO.UK Domain
.CO.UK Domain Linux Hosting
Linux Hosting Windows Hosting
Windows Hosting